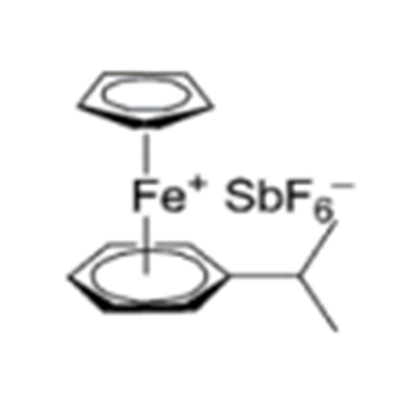
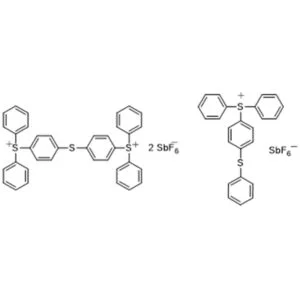
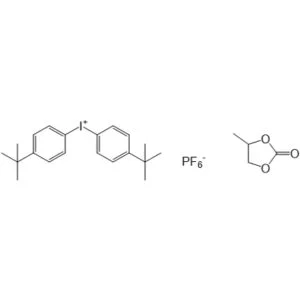
Photoinitiator 262 Application Scenarios
1. Cationic Photopolymerization Initiators:
Used in UV-curing epoxy resins, vinyl ethers, and other systems, such as UV-curing coatings, inks, adhesives, and electronic packaging materials. Exposure to UV light generates acid, initiating cationic polymerization and improving curing efficiency and coating performance (hardness, adhesion, chemical resistance).
2. Photoacid Generators (PAGs) for Photoresists:
As the core PAG in chemically amplified photoresists, suitable for g-line, i-line, and other UV lithography processes. Used in the micron-level pattern fabrication of semiconductors, LCDs, and PCBs. Exposure to UV light generates acid, initiating resin crosslinking or degradation, enabling pattern transfer.
3. Curing of Microelectronic Materials:
Used in the photocuring of microelectronic packaging adhesives, dielectric materials, and printed circuit board (PCB) solder mask inks, contributing to the high-precision manufacturing and improved reliability of electronic components.
4. Fine Chemicals and Organic Synthesis:
Used as an acid source catalyst in organic synthesis for specific acid-catalyzed reactions (such as etherification, condensation, and cyclization reactions), and in the synthesis and modification of functional polymer materials, providing a controllable acidic environment.
5. 3D-Druck-Materialien:
Applied in the resin formulations of photopolymerization 3D printing (SLA/DLP) as a cationic initiator, improving the mechanical strength, heat resistance, and dimensional accuracy of printed parts, meeting the demands of high-performance 3D printing.