Description
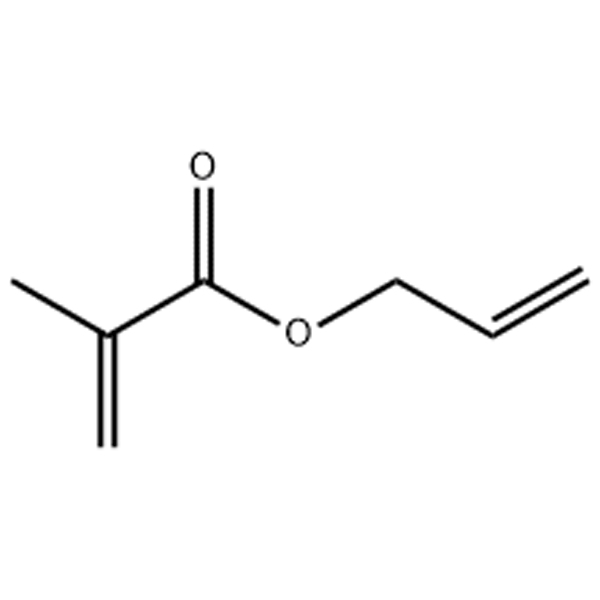
AMA Monomer / Allyl methacrylate CAS 96-05-9
| Item | Specification |
| CAS No | 96-05-9 |
| Color(Pt-Co),Hazen | 20 |
| Pueity,% ≥ | 99.5 |
| Water content,% ≤ | 0.1 |
| VAcidity(as methacrylic acid),% ≤ | 0.03 |
Allyl methacrylate is an important cross-linking agent that provides second-stage effective cross-linking of bifunctional groups with good pharmaceutical resistance, impact strength, adhesion, hardness and low shrinkage. It is used in dental materials, industrial paints, silicone intermediates, antiglare agents, optical polymers, elastomers and some vinyl and acrylate polymer systems.
Other Name:
Ageflex AMA;
Allylester kyseliny methakrylove;
allyl 2-methacrylate;
Allylmethacrylate;
Visomer AMA;
Contact Us Now!
If you need Price and Sample Testing, please fill in your contact information in the form below, we will usually contact you within 24 hours. You could also email me info@changhongchemical.com during working hours ( 8:30 am to 6:00 pm UTC+8 Mon.~Sat. ) or use the website live chat to get prompt reply.
| CHLUMICRYL® AAEM Monomer | CAS 21282-97-3 | Acetylacetoxyethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® ADAMA Monomer | CAS 16887-36-8 | 1-Adamantyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® AMA Monomer | CAS 96-05-9 | Allyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® BDDMA | CAS 2082-81-7 | 1,4-Butanedioldimethacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® BDDMP Monomer | CAS 92140-97-1 | 1,4-Butanediol Di(3-mercaptopropionate) |
| CHLUMICRYL® Bis-GMA Monomer | CAS 1565-94-2 | Bisphenol A Glycidyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® BZA Monomer | CAS 2495-35-4 | benzyl prop-2-enoate |
| CHLUMICRYL® BZMA Monomer | CAS 2495-37-6 | Benzyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® CHA Monomer | CAS 3066-71-5 | cyclohexyl prop-2-enoate |
| CHLUMICRYL® CHMA | CAS 101-43-9 | Cyclohexyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DCPA Monomer | CAS 12542-30-2 | Dihydrodicyclopentadienyl Acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DCPEMA Monomer | CAS 68586-19-6 | Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DCPMA Monomer | CAS 30798-39-1 | Dihydrodicyclopentadienyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DEAEA Monomer | CAS 2426-54-2 | 2-(diethylamino)ethyl prop-2-enoate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DEAM Monomer | CAS 105-16-8 | Diethylaminoethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DMAEA Monomer | CAS 2439-35-2 | Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DMAEMA | CAS 2867-47-2 | N,M-Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DMES | CAS 3570-55-6 | 2,2′-Thiodiethanethiol/Bis(2-mercaptoethyl) sulfide/Dimercapto diethyl sulfide/THIOCURE DMDS/Polythiol DMDS/Mercaptan DMDS |
| CHLUMICRYL® DMPT | CAS 131538-00-6 | THIOCURE DMPT |
| CHLUMICRYL® ECPMA Monomer | CAS 266308-58-1 | 1-Ethylcyclopentyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EEMA | CAS 2370-63-0 | 2-ethoxyethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EGDMA Monomer | CAS 97-90-5 | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EGDMP Monomer | CAS 22504-50-3 | Ethylene glycol Bis(3-mercaptopropionate) |
| CHLUMICRYL® EHMA | CAS 688-84-6 | 2-Ethylhexyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EMA Monomer | CAS 97-63-2 | Ethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EO10-BPADA Monomer | CAS 64401-02-1 | ethoxylated bisphenol A diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EO4-BPADA Monomer | CAS 64401-02-1 | ethoxylated bisphenol A diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® HDCPA Monomer | CAS 79637-74-4 | Dicyclopentenyl acrylate (hydrogenation) |
| CHLUMICRYL® IBA Monomer | CAS 106-63-8 | Isobutyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® i-BMA | CAS 97-86-9 | Isobutyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® MCPMA Monomer | CAS 178889-45-7 | 1-Methylcyclopentyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® MEMA | CAS 6976-93-8 | 2-Methoxyethyl Methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® MPEG Monomer | CAS 26915-72-0 | MPEG Monomer |
| CHLUMICRYL® Muscomer Tricyclodecanedimethanol | CAS 26896-48-0 | Muscomer Tricyclodecanedimethanol |
| CHLUMICRYL® N,N-Dimethyl Acrylamide | CAS 2680-03-7 | N,N-Dimethyl Acrylamide |
| CHLUMICRYL® n-BMA | CAS 97-88-1 | n-Butyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® PETMP Monomer | CAS 7575-23-7 | PETMP Monomer |
| CHLUMICRYL® Polythiol PM839 | CAS 72244-98-5 | Polythiol PM839 |
| CHLUMICRYL® TBAEMA | CAS 3775-90-4 | 2-(Tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® THFMA Monomer | CAS 2455-24-5 | Tetrahydrofurfuryl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® ACMO Monomer | CAS 5117-12-4 | 4-acryloylmorpholine |
| CHLUMICRYL® DCPEOA Monomer | CAS 65983-31-5 | Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl Acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DI-TMPTA Monomer | CAS 94108-97-1 | DI(TRIMETHYLOLPROPANE) TETRAACRYLATE |
| CHLUMICRYL® DPGDA Monomer | CAS 57472-68-1 | Dipropylene Glycol Dienoate |
| CHLUMICRYL® DPHA Monomer | CAS 29570-58-9 | Dipentaerythritol hexaacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EO3-TMPTA Monomer | CAS 28961-43-5 | Ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® EOEOEA Monomer | CAS 7328-17-8 | 2-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)ethyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® GPTA ( G3POTA ) Monomer | CAS 52408-84-1 | GLYCERYL PROPOXY TRIACRYLATE |
| CHLUMICRYL® HDDA Monomer | CAS 13048-33-4 | Hexamethylene Diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® HEMA Monomer | CAS 868-77-9 | 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® HPMA Monomer | CAS 27813-02-1 | 2-Hydroxypropyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® IBOA Monomer | CAS 5888-33-5 | Isobornyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® IBOMA | CAS 7534-94-3 | Isobornyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® IDA Monomer | CAS 1330-61-6 | Isodecyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® IPAMA Monomer | CAS 297156-50-4 | 2-isopropyl-2-adamantyl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® LMA Monomer | CAS 142-90-5 | Lauryl methacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® NP-4EA Monomer | CAS 50974-47-5 | (4) ethoxylated nonylphenol |
| CHLUMICRYL® NPGDA Monomer | CAS 2223-82-7 | Neopentyl glycol diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® PDDA | Phthalate diethylene glycol diacrylate | |
| CHLUMICRYL® PEGDA Monomer | CAS 26570-48-9 | Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® PEGDMA Monomer | CAS 25852-47-5 | Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® PETA Monomer | CAS 3524-68-3 | PETA; 2-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-[[(1-oxoallyl)oxy]methyl]-1,3-propanediyl diacrylate; 3-(acryloyloxy)-2-[(acryloyloxy)methyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)propyl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® PHEA Monomer | CAS 48145-04-6 | 2-PHENOXYETHYL ACRYLATE |
| CHLUMICRYL® PO2-NPGDA | CAS 84170-74-1 | |
| CHLUMICRYL® TEGDMA Monomer | CAS 109-16-0 | Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® THFA Monomer | CAS 2399-48-6 | Tetrahydrofurfuryl acrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® TMPTA Monomer | CAS 15625-89-5 | Trimethylolpropane triacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® TMPTMA Monomer | CAS 3290-92-4 | Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® TPGDA Monomer | CAS 42978-66-5 | Tripropylene glycol diacrylate |
| CHLUMICRYL® UV Functional Monomers | Acrylic Monomers |



Alexander Lee –
From start to finish, the entire shopping experience was seamless. The product arrived well-packaged and in pristine condition. A definite five-star!