Quels sont les principaux composants chimiques des encres d'impression UV? ?

Understanding the main parts of UV printing inks helps you learn how the UV Printing Process and Ink Analysis work. These inks have monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, pigments, and additives. Each part has a special job in printing. The table below shows how these parts change how the ink works and how safe it is:
| Component Type | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Oligomères | Make the ink bend easily and stick well |
| Reactive Diluents | Change how thick the ink is and help it dry fast |
| Photoinitiateurs | Begin the drying process when UV light shines on them |
| Pigments/Dyes | Give the ink color and help it stay strong |
| Additifs | Help the ink spread smoothly and stick better, even in small amounts |
These parts help the ink dry fast, last longer, and make less air pollution.
Principaux enseignements
- UV printing inks have five main parts: monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, pigments, and additives. Each part is important for how the ink works.
- Monomers and oligomers decide how thick and bendy the ink is. They help the ink dry fast and make a strong print.
- Photoinitiators are needed to start the drying process. They react to UV light and change the ink from liquid to solid very quickly.
- Pigments give UV inks bright colors and stop them from fading. Good pigments make prints last a long time.
- Additives make UV inks work better. They help the ink spread well, stick more, and not fade, so prints stay nice for a long time.
UV Ink Composition

You can learn about uv ink composition by looking at the main chemical groups in these inks. Each group has a special job in how the ink works and cures under uv light. The main parts are monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, pigments, and additives. These parts work together to help the ink dry fast, look bright, and make strong prints.
Monomers and Oligomers
Monomers and oligomers are the main building blocks of uv inks. Monomers act as reactive diluents. They help control if the ink is thick or thin. They also make the curing process faster. Oligomers form the main film when the ink dries. They decide how flexible, tough, and sticky the print will be.
- Monomers change how thick the ink is and help it cure fast.
- Oligomers make the main structure of the dried ink. They give the ink strength and flexibility.
Acrylates and nitrogen-containing monomers are very important in uv ink composition. They help the ink cure quickly and stick well to many surfaces. The table below shows some common types you will see in inkjet formulation design:
| Monomer Name | Type |
|---|---|
| UrDMA | Urethane Dimethacrylate |
| UrA | Urethane Acrylate |
You will often see these monomers in uv light curing monomers. They help the ink flow well and make strong bonds.
Photoinitiateurs
Photoinitiators start the curing process. When uv light shines on the ink, these chemicals break apart. They create free radicals. Free radicals make the monomers and oligomers join together. This turns the liquid ink into a solid film.
Here is a table of common photoinitiators and where you might find them:
| Type | Photoinitiator Name | Typical Applications | Light Absorption Range (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I (Cleavage) | 1-Hydroxycyclohexyl phénylcétone | Coatings, inks, adhesives | ~245–330 |
| 2-Hydroxy-2-méthylpropiophénone | Clear coatings, 3D printing resins | ~240–320 | |
| Benzoin ether | UV inks, varnishes | ~250–340 | |
| Acyl phosphine oxide | Pigmented systems, white coatings | ~350–420 | |
| Bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)-phenylphosphine oxide | Thick films, dental composites | ~350–430 | |
| Type II (H-Abstraction) | Benzophénone | Inks, plastics, overprint varnishes | ~250–365 |
| Thioxanthone derivatives | Screen inks, UV flexo inks | ~350–420 | |
| Camphorquinone | Dental resins and composites | ~400–500 |
You should know that not all photoinitiators are safe for every use. If the ink does not cure all the way, some photoinitiators can move into food or other products. This is a big problem for food packaging. For example, in 2005, there was a big recall. A photoinitiator called isopropyl thioxanthone (ITX) moved from the ink into baby milk. Because of this, countries like Switzerland made rules to control which photo-initiators can be used in inks for food packaging.
Pigments and Additives
Pigments and additives give uv inks their color and special features. Pigments are tiny solid pieces that stay in the ink. They make the colors strong, bright, and last a long time. Additives help the ink flow smoothly, stick better, and last longer.
| Aspect | Influence on UV Printing Inks |
|---|---|
| Color Strength | High-quality pigments provide strong color strength, allowing for vibrant colors with less ink usage. |
| Opacité | Pigments with high hiding power ensure proper coverage on various substrates, enhancing design clarity. |
| Taille des particules | Fine, well-dispersed pigments lead to smoother ink flow and sharper image edges. |
| Solidité à la lumière | Quality pigments resist fading under light exposure, ensuring long-lasting color stability. |
Pigments are not the same as dyes. Pigments stay as solid pieces, so they do not fade as fast as dyes. This means your prints will look bright and clear for a long time. The type and quality of pigment also affect how well the ink resists fading. Inorganic pigments like titanium white and chrome yellow are very good at standing up to uv light.
Additives are a small part of the chemical composition, but they are important. They can help the ink dry faster, stop clogs in the printer, and keep the colors from fading.
You can see how much of each part is in a typical uv ink composition in the chart below:
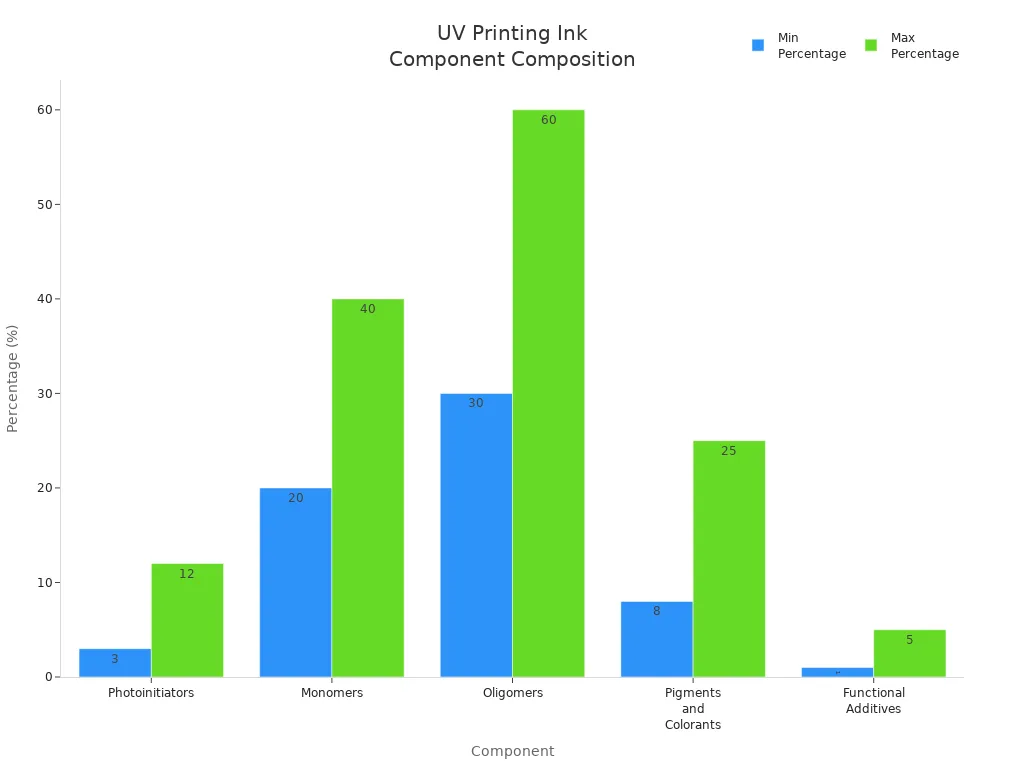
When you look at uv ink composition, you see that each part has a clear job. Monomers and oligomers build the structure. Photoinitiators start the curing. Pigments and additives give color and improve how the ink works. Knowing about these parts helps you pick the right ink for your needs.
UV Curable Inks: Key Chemical Groups
Prepolymers and Monomers
Prepolymers and monomers are the main parts of uv curable ink. Prepolymers are special resins with double bonds. These bonds help the ink react fast when uv light hits it. Most prepolymers in uv curable ink are acrylic resins. They make the ink cure quickly and give it strength. Monomers are also called reactive diluents. They change how thick or thin the ink is. Monomers also help decide how the cured film feels and works.
- Prepolymers build the main structure of the cured ink.
- Monomers make the ink easy to print and cure fast.
- Picking different prepolymers and monomers changes how tough and bendy the ink is.
You can see how different resins change uv curable ink in this table:
| Resin Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Epoxy Acrylic Resin | Easy to make, low cost, cures fast, hard, shiny, and stands up to chemicals and heat. |
| Polyurethane Acrylic | Very strong, flexible, tough, and sticks well to many surfaces. |
| Polyester Acrylic | Does not smell much, gentle, bends well, and mixes with pigments. |
If you use UDMA prepolymer in polyurethane films, your prints get stronger. Cross-linking in the polyurethane network makes the ink more water-resistant and less likely to break.
The ink uses the thiol-ene click reaction. Thiol groups react with vinyl double bonds when uv light shines on them. The photoinitiator DMPA makes free radicals. These free radicals start cross-linking. This builds a strong network that gives the printed material its strength.
Photoinitiator Function
Photoinitiators are very important in uv curable ink. When uv light shines on the ink, photoinitiators soak up the energy. They break apart and make free radicals. These free radicals start a chain reaction. This reaction links the monomers and prepolymers together. The liquid ink turns into a solid film. The kind of photoinitiator you pick changes how fast and well the ink cures.
UV curing uses strong light, usually between 240 and 420 nm. Photoinitiators take in this light and start the polymerization process. Some photoinitiators, like 1173, work really well. They help the ink cure fast and keep colors bright. If you want no yellowing and quick results, pick these high-efficiency photoinitiators.
Additives in UV Curable Ink
Additives help uv curable ink work better for different jobs. You can add special chemicals to improve flow, flexibility, and stability. Some additives help the ink resist water and chemicals. Others help the ink stick to many surfaces.
- M-313 makes the ink last longer and stronger.
- M-5700 makes the ink more flexible and helps it cure fast.
- M-930 makes the ink thinner and helps it fight chemicals.
- Leveling agents give a smooth finish.
- Defoamers stop bubbles from forming.
- Adhesion promoters help the ink stick to many things.
You will also find surfactants and stabilizers in some inkjet recipes. These additives help uv curable ink stay stable and print well. When you pick the right additives, your prints last longer and look better. Additives also help uv inks stand up to sunlight, water, and handling. This makes uv curable inks a smart choice for many printing needs. Each part of the formula works together to give you fast curing and strong prints.
UV Printing Process and Ink Analysis

Chemical Reactions During Curing
When you use uv curable ink, a special reaction starts. The ink has monomères, oligomers, and photoinitiators. UV light shines on the ink. Photoinitiators soak up the energy and make free radicals. These free radicals help monomers and oligomers link together. This makes a strong, crosslinked network. The ink dries right away and sticks well to things. You do not need heat or solvents, so curing happens at low temperatures. This makes uv curable ink good for printing on many surfaces.
- Monomers and oligomers decide if the print is flexible or tough.
- Photoinitiators help the ink cure fast and even.
- Pigments add color, but they can block uv light, so you need the right mix for good prints.
Impact on Performance and Safety
The uv printing process and ink analysis show how the ink’s chemicals affect how it works. The right monomers and oligomers give strong prints that stick well. Photoinitiators must match the uv lamp to cure the ink all the way. Additives help the ink flow and stick better. You can see the results in the table below:
| Paramètres | Valeur |
|---|---|
| Adhésion | 98% |
| Brillant | 50 GU |
| Minimum curing time | 0.7 s |
| Durabilité | Haut |
| Performance | Bon |
Safety is important when you use uv curable ink. UV light can hurt your skin and eyes if you are not careful. Breathing in ink mist or ozone from uv lamps can cause health problems. Some chemicals in the ink, like acrylates, can cause allergies. You should wear gloves and make sure there is good airflow to stay safe.
Environmental Considerations
The uv printing process and ink analysis also show how the ink affects the environment. UV curable ink gives off very few VOCs, much less than old inks. This means less air pollution and a safer place to work. The curing process does not use evaporation, so almost all the ink stays on the print. Some chemicals, like photoinitiators, can hurt fish and other water life if not handled right. Cured ink lasts a long time, but it is hard to recycle. Groups like the EPA and FDA make rules to keep uv curable ink safe for people and nature. You must follow these rules when printing on different things.
Tip: Wear splash-proof gloves and cover uv lamps to stop leaks. Always check if your ink is safe for food packaging and follows environmental rules.
Analytical Methods
You can study the uv printing process and ink analysis with many tools. These include FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and chromatography. These tools help you check what is in the ink and make it work better. When you test the ink, you can help it last longer and print well.
You now know that UV printing inks have five main parts. Each part helps make prints look good and safe to use.
| Component | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Monomères | Control flexibility and adhesion |
| Oligomères | Build strength and resistance |
| Photoinitiateurs | Start the curing process under UV light |
| Pigments | Add color and prevent fading |
| Additifs | Improve flow, adhesion, and print consistency |
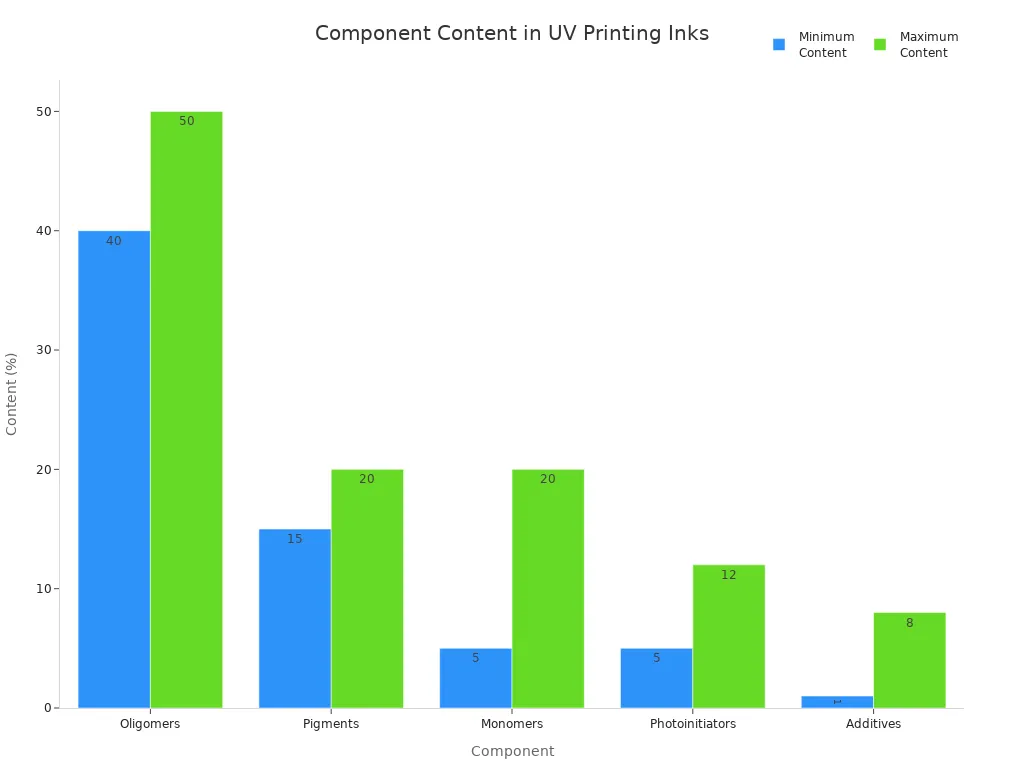
If you learn about UV ink chemistry, you can pick inks that work well. This helps keep you safe and helps the planet. Knowing what is in your ink lets you make better choices when printing.
FAQ
What makes UV printing inks different from regular inks?
You use UV printing inks because they dry fast under UV light. Regular inks need heat or air to dry. UV inks also make prints stronger and more colorful.
Are UV printing inks safe to use?
You stay safe if you wear gloves and work in a well-ventilated area. Some chemicals can cause skin irritation. Always follow safety instructions on the ink label.
Conseil : Check if your ink is food-safe before printing on packaging.
Can you recycle prints made with UV inks?
You may find it hard to recycle prints with UV inks. The cured ink forms a tough layer that does not break down easily. Always check local recycling rules.
Why do UV inks use photoinitiators?
Photoinitiators help your ink dry instantly when you shine UV light on it. They start a chemical reaction that turns the liquid ink into a solid film.
